



NATPHARMACO,LLC |7550 Creedmor Rd Ste 104#1018 | Raleigh NC | 27613 | Tel: +1 919-714-9291
Copyright All Rights Reserved By NATPHARMACO,LLC


Cardiovascular Diseases:
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally,
taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year. CVDs are a group of
disorders of the heart and blood vessels and include coronary heart disease,
cerebrovascular disease, rheumatic heart disease and other conditions.
Types Of Heart Diseases
Cancer:
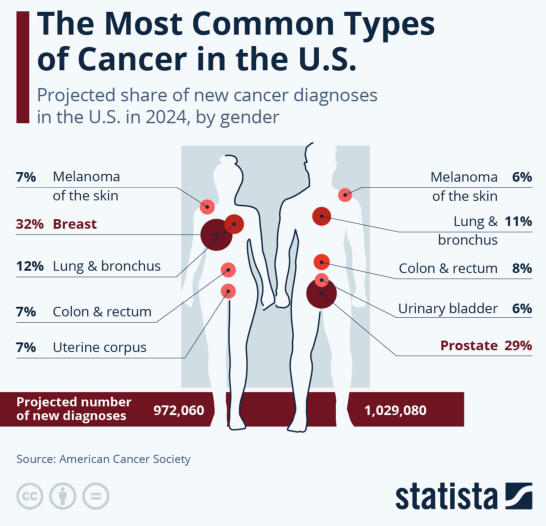
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the most common types of
cancer in 2020 were breast, lung, colon and rectum, prostate, non-melanoma
skin, and stomach. In the United States, breast, lung and bronchus, prostate,
and colorectal cancers account for almost 50% of all new cancer cases.
Other common types of cancer include:
- Carcinomas: The most common type of cancer, which includes many breast,
lung, bowel, and prostate cancers
- Melanoma: A type of skin cancer that starts in the melanocytes, which are cells
that produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color
- Blood cancer: A group of cancers that occur when blood cells don't develop
properly
Common Cancer TypesCommon Cancer Types
- Bladder Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Skin Cancer
- Uterine Cancer
High Blood Pressure:
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can be caused by a number of
factors, including lifestyle choices, health conditions, and medications:
- Lifestyle choices: These include:
- Unhealthy diet, such as eating too much salt, saturated fat, and trans fats,
and not enough fruits and vegetables
- Physical inactivity
- Consuming tobacco and alcohol
- Being overweight or obese
- Lack of sleep
- Stress
- Using substances like cocaine, methamphetamine, or "bath salts"
- Health conditions: These include:
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Thyroid disease
- Pregnancy
- Medications: These include medications prescribed for high blood pressure, as
well as other medications
Other factors that can increase the risk of high blood pressure include:
- Family history
- Age over 65
- Race or ethnicity, such as Black African or Black Caribbean descent
- Living in a deprived area
High blood pressure usually develops over time and can lead to serious health
problems that affect the heart, brain, kidneys, and eyes. Managing blood
pressure can help lower the risk of these problems.
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, can have several risks,
including:
- Falls
Dizziness and fainting caused by low blood pressure can lead to falls, which can
result in broken bones, concussions, and other serious injuries. In older adults,
falls can also lead to a broken hip or spine fracture, which can reduce their
health and ability to move around.
- Shock
When blood pressure drops too low, vital organs don't receive enough oxygen
and nutrients, which can lead to shock. Shock occurs when the body begins to
shut down due to limited blood flow and oxygen, and requires immediate
medical attention. Symptoms of shock include cold and sweaty skin, rapid
breathing, a blue skin tone, a weak and rapid pulse, and confusion, especially in
older people. If you have symptoms of shock, call 911 right away.
- Organ damage
Sudden, severe drops in blood pressure can starve the body of oxygen, which
can damage the heart, brain, and other organs.
- Heart problems or stroke
Low blood pressure can cause the heart to try to compensate by pumping
faster or harder, which can lead to problems like heart failure, stroke, or deep
vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Vision loss
Severe low blood pressure can also cause blurred vision, which can be
dangerous if you're driving. In this case, you should find a place to sit down and
rest until your blood pressure and vision return to normal.
Diabetes:
There is no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed and reversed in most
people.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that can be managed by a medical professional
to improve symptoms. Treatments include:
- Blood sugar control: Using diet, oral medications, or insulin to manage blood
sugar levels
- Lifestyle changes: Increasing physical activity, not smoking, getting enough
sleep, limiting alcohol, and managing stress
- Regular screening: Checking for complications with lab tests
Reversing diabetes means managing blood sugar levels to the point where
medications are no longer needed, and maintaining that level through a healthy
lifestyle. For type 2 diabetes, this can be achieved through remission, which is
when glucose levels return to a non-diabetes range. However, remission is not
permanent. Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass or gastric sleeve, may also
be an option for people with type 2 diabetes who are obese and have had the
disease for five years or less. While surgery carries serious risks, most people
who have it done end up reversing their diabetes.
Hepatitis diseases:
There is no cure for hepatitis once it occurs, but treatment can help prevent
further damage to the liver, reverse existing damage, and relieve symptoms.
Hepatitis A and E are usually resolved without treatment, but hepatitis B, C, and
D can become chronic and lead to serious health issues.
Here's some information about hepatitis treatments for specific types:
- Hepatitis A and E
People with these types of hepatitis usually recover without treatment.
- Hepatitis B
Most adults recover fully, but infants and children are more likely to develop a
chronic infection. There are approved antivirals, such as entecavir, tenofovir
(TDF), and tenofovir (TAF), that can help treat hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis C
Direct-acting antiviral medicines (DAAs) can cure more than 95% of people with
hepatitis C, but access to diagnosis and treatment is limited.
- Autoimmune hepatitis
Medications can help control an overactive immune system and prevent
further attacks on the liver.
Hepatitis can be spread through contaminated food and water, blood products,
and contact with infected people. To prevent hepatitis, you can:
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
- Wash your hands regularly
- Avoid contact with infected people
- Avoid contaminated body fluids, food, and water
Kidney disease:
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and kidney failure (ESRD) are usually not curable,
but treatments can help relieve symptoms and slow down the damage.
Treatments depend on the stage of the disease and can include:
- Lifestyle changes
Staying hydrated, eating less protein, and avoiding pain pills can help.
- Medications
Depending on the cause of the disease, a doctor may prescribe medications to
help with blood pressure, cholesterol, fluid levels, and more.
- Dialysis
A mechanical process that removes toxins and waste from the body. Dialysis
may be necessary in advanced stages of CKD or ESRD.
- Kidney transplant
A major surgery that may be necessary in advanced stages of CKD or ESRD. A
successful transplant means you won't need dialysis, but you'll need to take
medication to help your body accept the donated kidney.
HIV:
Can HIV be cure?n HIV be cure?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) can treat and control infection with HIV, the virus
that causes AIDS. People who take these medications can reduce the amount of
the virus in their bodies so much that blood tests don't even show it's there.
They can live long, healthy lives. They're less likely to pass the virus to others.
But even if you take ART drugs as prescribed, an inactive form of the virus still
lives in groups of cells in your body called HIV reservoirs. If you stop taking ART,
the virus in the reservoirs can become active again and lead to AIDS. There's still
no general cure for HIV infection, although a handful of people across the world
have become HIV-free after having risky stem cell transplants to treat cancer.
You may see or hear claims that certain herbal medicines, devices, or chemicals
can cure HIV. But no natural or alternative remedy can cure or effectively treat
HIV. Some herbal medications can even keep antiretroviral drugs from working
as they should.
Although we've gone 40 years without a cure for HIV, scientists believe one is
possible. They're researching several ways to make that happen. Read more
Why Is It So Difficult to Find an HIV Cure?
The silent HIV epidemic has been ongoing for 4 decades.
AIDS-related illnesses have claimed over 32 million lives since the beginning of
the HIV epidemic in 1981. The death toll, societal impact, and economic effects
of the HIV epidemic have made HIV/AIDS one of the greatest public health
threats the world has ever known. Governments, companies and private
individuals have collectively spent trillions of dollars on the development of
effective treatments and the search for an effective vaccine or a cure. Today,
antiretroviral medications (ART) make HIV a manageable condition, but neither
a vaccine nor a cure are available. However, the fight for a cure isn’t over, and
new biotechnologies may finally provide a definitive remedy for people living
with HIV. READ MORE...
Cases of HIV cure...
Key points
- Cases of HIV cure are exceptional, though there are also some cases of long-
term control of HIV without having to take treatment.
- Three people are confirmed to have been cured of HIV after stem cell
transplants replaced all the cells of their immune systems. Another three
similar cases have been reported but it is too early to say if HIV has been
completely cleared in these cases.
- Several cases of HIV control after stopping treatment have been reported. In
these people, HIV may still be present at extremely low levels but it is being
controlled by elements of the immune system.
- There are also a few cases of exceptional HIV control in people who have never
taken antiretroviral treatment.
This page provides information on people who have been cured of HIV or appear
able to control the virus without treatment. These cases have all been reported
by scientists in medical journals or at scientific conferences. Sometimes, people
are described as having long-term viral control without antiretroviral therapy
(ART) or being in ‘remission’. This reflects uncertainty about whether HIV levels
might eventually rebound.
While these cases are unusual, a major focus of HIV cure research involves
finding out how these people manage to control their HIV, and developing
therapies to help more people do the same thing. READ MORE..
Alzheimer:Alzheimer:
Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia. It is a progressive
disease beginning with mild memory loss and possibly leading to loss of the
ability to carry on a conversation and respond to the environment. Alzheimer's
disease involves parts of the brain that control thought, memory, and language.
There's no cure for Alzheimer's, but there are treatments that may change
disease progression, and drug and non-drug options that may help treat
symptoms. Understanding available options can help individuals living with the
disease and their caregivers to cope with symptoms and improve quality of life.
Infertility Diseases:
What is the disease associated with infertility?
Premature ovarian insufficiency, polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis,
uterine fibroids and endometrial polypsmay play a role in female infertility.
Male infertility may be due to testicular and post-testicular deficiencies.
These can include:
- Ovulation disorders. These conditions affect the release of eggs from the
ovaries. ...
- Conditions of the uterus. ...
- Fallopian tube damage or blockage. ...
- Endometriosis. ...
- Primary ovarian insufficiency. ...
- Pelvic adhesions. ...
- Cancer and its treatment.
EyeSight Diseases:
The 5 most common eye problems
1. Dry Eye. Dry eye is one of the most common eye problems. ...
2. Diabetic Retinopathy. Retinopathy is the most common eye problem in people
with diabetes. ...
3. Cataracts. As we age, the lenses in our eyes can become cloudy. ...
4. Glaucoma. ...
5. Macular Degeneration.
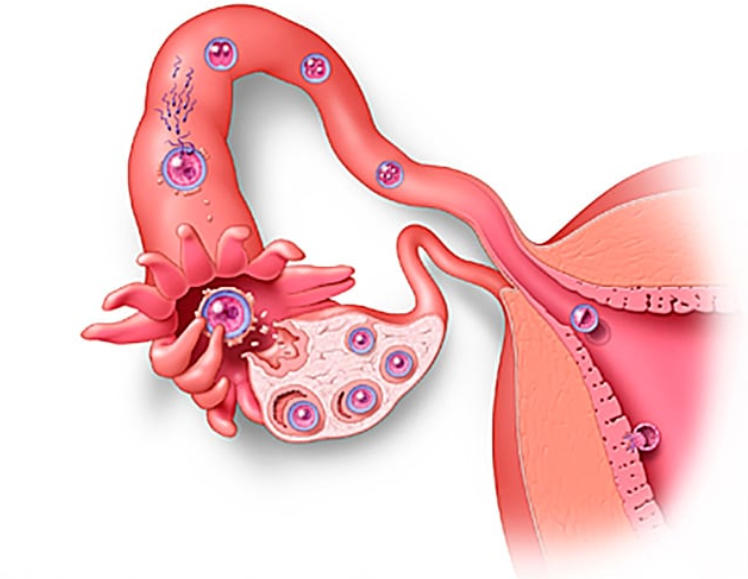
Ovarian Cyst & Fribroma (Fibroid Cyst)
Know The Difference Between Cysts and Fibroids?
A fibroid cyst is a growth that forms on the ovaries when hormones are released
from an egg. Fibroids and cysts can affect a woman's reproductive system in
different ways, but they can have similar symptoms, such as pelvic pain and
abnormal uterine bleeding. Both conditions can also affect fertility and are
usually diagnosed by an ultrasound scan.
Here are some differences between fibroids and cysts:
- Composition
Fibroids are made of smooth muscle tissue, while cysts are fluid-filled pockets.
- Location
Fibroids are found in or on the uterus, while cysts are often found in the
ovaries, but can also be present in the fallopian tubes and vaginal wall.
- Cancerous potential
Fibroids are almost always benign, while cysts are often benign as well, but
cancer can sometimes cause a cyst. For example, in some postmenopausal
women, an ovarian cyst can develop into a malignant cancer growth.
Symptoms of fibroids and cysts can include:
- Fibroids
Pain, heavy or irregular vaginal bleeding, pressure during urination, bloating,
and a protruding abdomen
- Cysts
Pain, breast soreness, menstrual pain, difficulty urinating, and sudden severe
pain
Treatment for fibroids and cysts depends on the symptoms, plans for a family,
and can include non-surgical or surgical intervention. Regular pelvic exams can
also help monitor for these growths.
Sleeping Disorders & Meds (Somniferes)
There are several different types of sleep-wake disorders, of which insomnia is
the most common. Other sleep-wake disorders include obstructive sleep apnea,
parasomnias, narcolepsy, and restless leg syndrome. Sleep difficulties are linked
to both physical and emotional problems.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases:
Eight pathogens are linked to the greatest incidence of STIs. Of these, 4 are
currently curable: syphilis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia and trichomoniasis.
The other 4 are viral infections: hepatitis B, herpes simplex virus (HSV), HIV and
human papillomavirus (HPV)
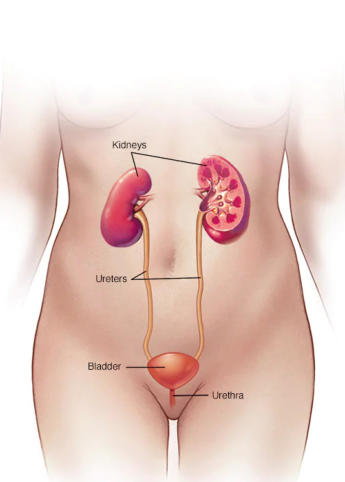
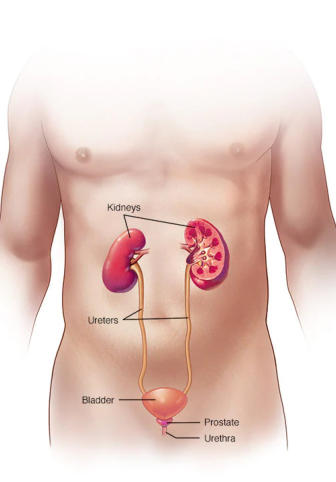
Urinary Tract Infection: A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part
of the urinary system. The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder
and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and
the urethra. Women are at greater risk of developing a UTI than are men.

List of Diseases that our Plant-Based Formulas Can
Treat and Cure:


Vaginal Yeast Infection: A vaginal yeast infection is a fungal infection that causes
irritation, discharge and intense itchiness of the vagina and the vulva — the tissues
at the vaginal opening. Also called vaginal candidiasis, vaginal yeast infection affects
up to 3 out of 4 women at some point in their lifetimes. Many women experience at
least two episodes.
A vaginal yeast infection isn't considered a sexually transmitted infection. But, there's
an increased risk of vaginal yeast infection at the time of first regular sexual activity.
There's also some evidence that infections may be linked to mouth to genital contact
(oral-genital sex)
Infectious Diseases:
Types of Infections in the Body
Infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites, and can enter the
body through skin-to-skin contact or the transfer of body fluids.
- Viral infections
These can cause a wide range of diseases by interfering with cell function or killing
cells. Common viral infections include the common cold, flu, and upper respiratory
infections, which can cause symptoms like a runny nose, cough, sore throat, and
low-grade fever.
- Bacterial infections
These can cause illnesses like strep throat, urinary tract infections, meningitis, and
tuberculosis.
- Fungal infections
These can cause skin conditions like ringworm and athlete's foot, but some can
also infect the lungs or nervous system. Fungi release spores that can be inhaled or
picked up through direct contact, and tend to develop in warm, moist areas like the
groin, armpit, and feet.
- Parasitic infections
These can be caused by tiny parasites transmitted through mosquito bites or
animal feces. Some parasites don't noticeably affect people, while others can grow,
replicate, and invade organ systems
Corporate : +1 984 379 9200
Phytoclinic : +228 90 03 19 98
info@natpharmaco.com














